Harvesting
This integration is available through the hres_repo_harvest_claim plugin.
Haplo integrates with external systems to enable researchers to harvest items directly into the repository.
When harvested items are matched to an existing researcher profile, the system prompts the user to confirm or disclaim them.
To speed up metadata quality checks, repository editors are given clear notices in the user interface, indicating that the record was harvested from an external source, which external source the record was harvested from, and any fields that differ from the record already in the repository (if one exists).
Harvest claim framework
Once an output has been harvested from an external source Haplo attempts to match it to an existing output in the system, alongside matching any authors. If no authors can be matched the task will be delegated to the repository editors.
Once matched, the author(s) will get a task prompting them to view the output and either claim or disclaim this as their work. This task takes them to the screen shown below which displays tabs for each alternative version of the work from external sources. The metadata harvested from each source will be displayed on separate tabs, so authors and repository managers are able to view the output as it exists in external systems as well as the data within the repository.
These tabs are a convenient method to navigate between different versions of the output, however the “Authoritative version” is the version of record in Haplo. This version records the metadata and files displayed to researchers in the public repository and to external systems over metadata harvesting services such as OAI-PMH.
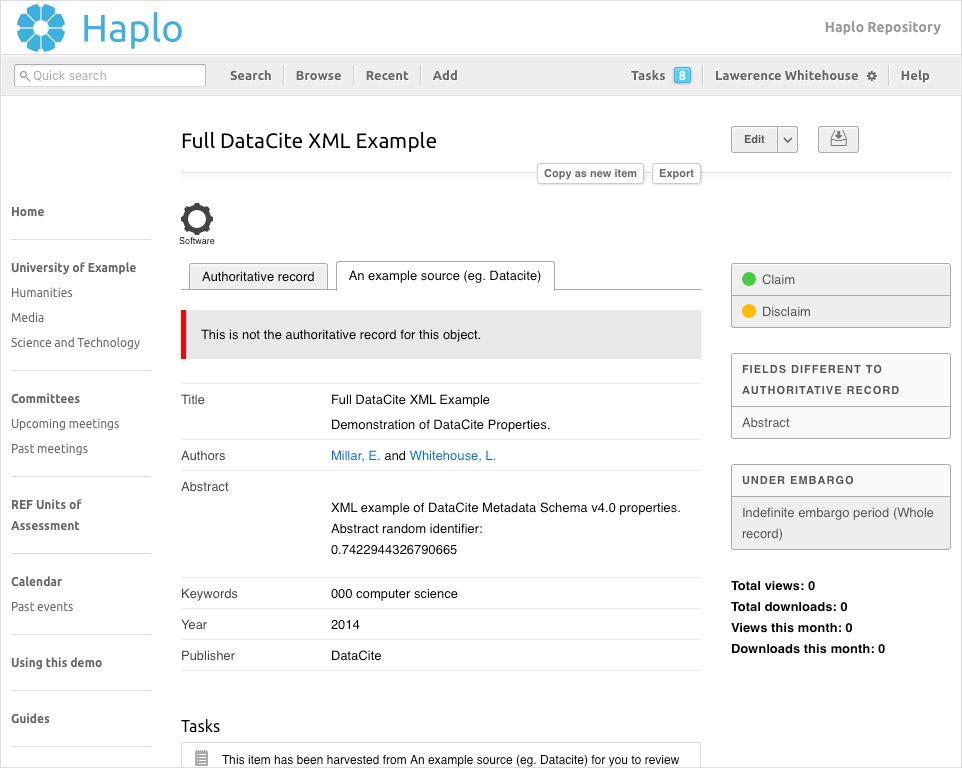
Only one author is required to claim an item. Once one author has claimed the output the task is removed for all other internal authors, and the output will be linked to all co-authors’ profiles. If the output is newly harvested into the repository it can then be submitted for deposit via the usual deposit workflow.
There are two possible actions to be taken by an author from this task and that is to Claim or Disclaim the output.
Disclaiming
This should be used if the harvested record has been incorrectly matched to an author. Disclaiming will remove them as a linked author, and if they were the only linked author it will delete the output from the repository and prevent it from being harvested again.
Claiming
This is the usual case, used when an output has been correctly matched to an author. The claim process will guide the user through a simple process to ensure the harvested record has enough information for the repository to automatically act on the harvest.
1. Author matching
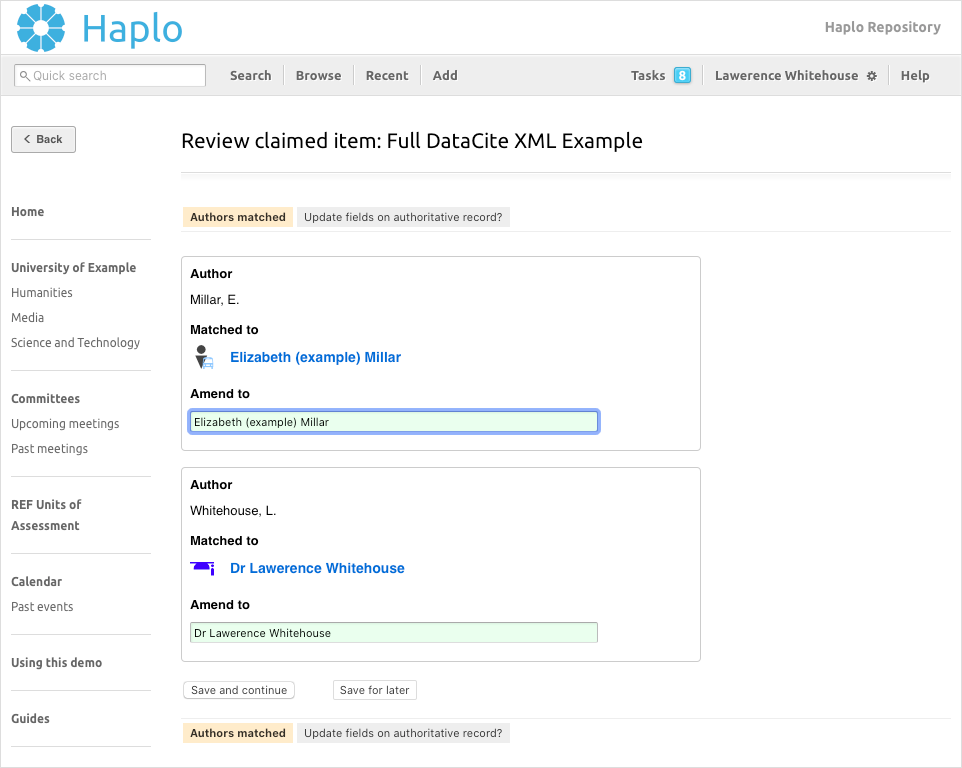
This form displays all authors in the citation string, the user they are currently linked to (if any) and the option to correct this link. If an author doesn’t have a record within the Haplo application this field can be left blank
If an external researcher record has been incorrectly created to record a co-author for a harvested item, and this is corrected to point to an internal researcher’s profile, all related harvested data will be migrated to the internal researcher’s record automatically.
2. Output match confirmation/manual matching
The next action will then depend on whether the system was able to find a match between the harvested output and an existing output in the repository.
- If a match has been found then the user will be asked to confirm that it is correct.
- If a match cannot be found, or the user rejects the matched output as correct, the user will be asked to either search for a correct match or move on if there is no matching output in the repository.
3. Attribute selection
Note: If there is no authoritative record matched this stage will be skipped and the harvested object will be used to create an authoritative version for the repository.
Finally the author will be asked to confirm which output they wish to use the values from, either the existing authoritative record or the harvested object. The system will display the attributes which differ between the two versions and would be changed if the user chooses to update the authoritative record.
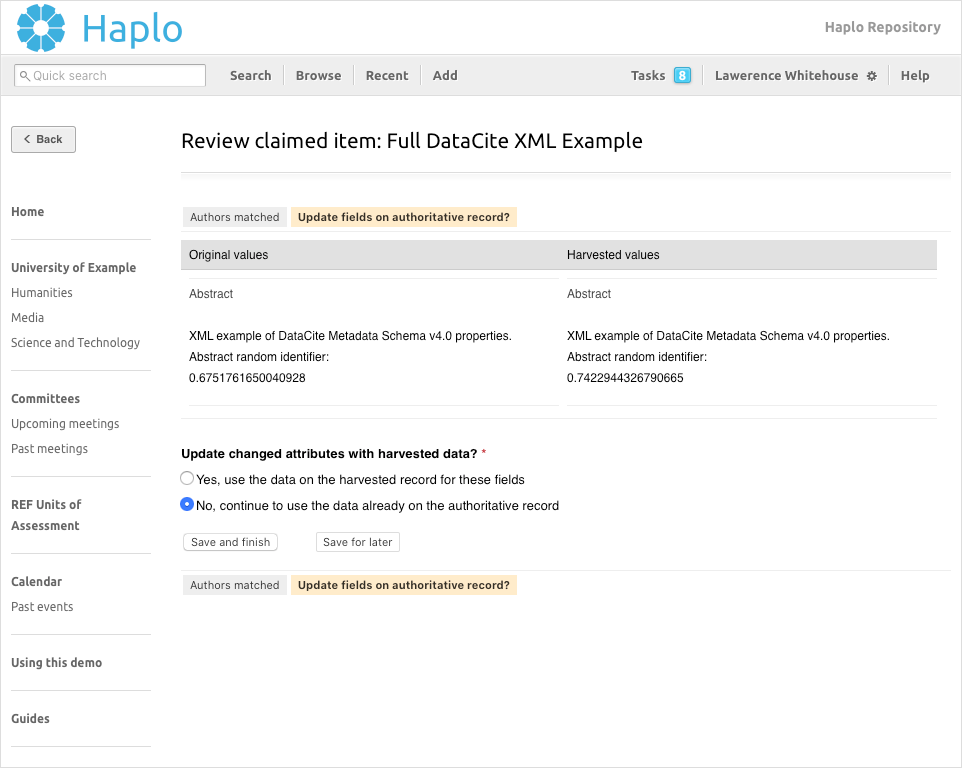
Keep values already on the authoritative record
- The authoritative record remains unchanged and the harvested object is displayed for reference.
Update the authoritative record with harvested metadata
- All of the metadata on the harvested record will be copied to the authoritative record, overwriting those fields on the authoritative record
Any additional metadata on the authoritative record will be left in place by this operation – only the fields present on the harvested record will be updated.
If only some of the fields should be used from the harvested record the authoritative record should be updated manually with these data, rather than use the automatic approach offered here for convenience.